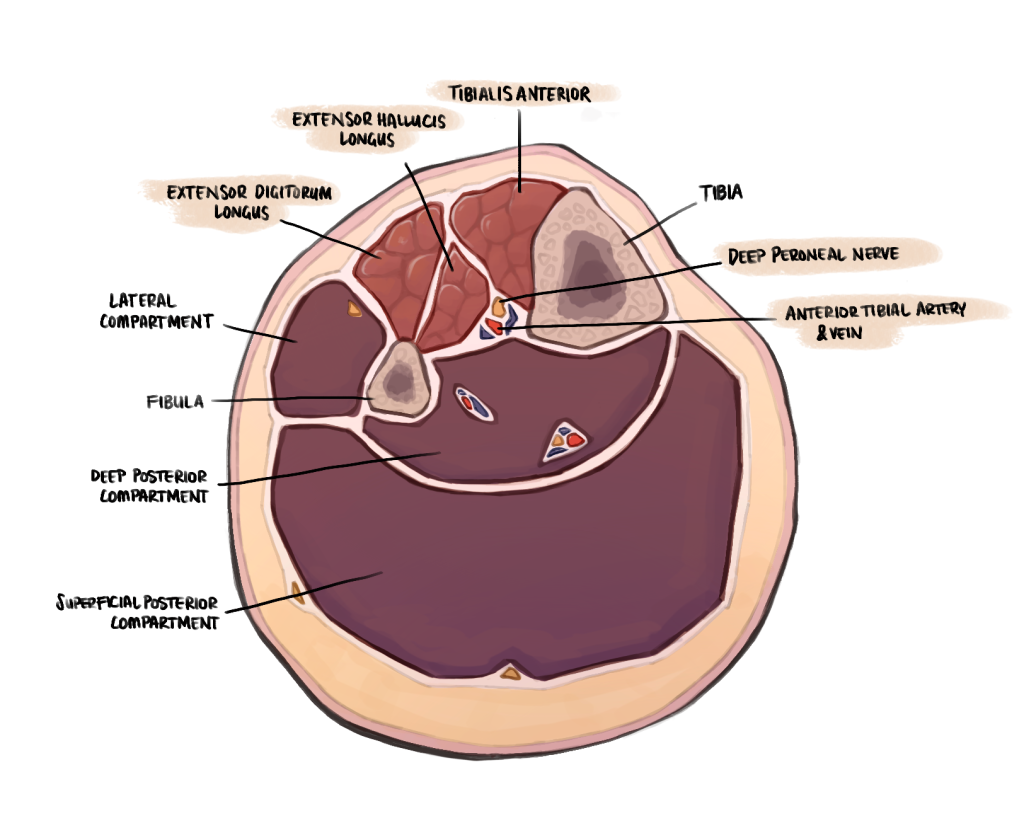
Credit: May Nichols (author’s illustration) – Anterior compartment of the leg and constituent structures
General
Boundaries
- Laterally: Anterior intermuscular septum of the leg and medial surface of fibula
- Anteriorly: Anterior deep fascia of the leg
- Medially: Lateral surface of tibia
- Posteriorly: Interosseous membrane
Function
- Dorsiflexion of the ankle
- Extension of big toe
- Extension of other toes
Muscles
Tibialis anterior (TA)
Origin
- Lateral surface of tibia and adjacent interosseous membrane.
Insertion
- Medial and inferior surfaces of medial cuneiform and adjacent surfaces on base of first metatarsal.
Innervation
- Deep peroneal nerve (DPN) (L4,5)
Function
- Dorsiflexion of foot at ankle joint
- Inversion of foot
- Contributor to maintenance of medial arch of foot
Extensor hallucis longus (EHL)
Origin
- Middle half of medial surface of fibula and adjacent surface of interosseous membrane.
Insertion
- Dorsal surface of base of distal phalanx of great toe
Innervation
- Deep peroneal nerve (L5,S1)
Function
- Extension of great toe
- Dorsiflexion and inversion of foot
- Tightening of subtalar joints
Extensor digitorum longus (EDL)
Origin
- Proximal two thirds of anterior surface of fibula, interosseous membrane and superior tibiofibular joint
Insertion
- via dorsal digital expansions into bases of distal and middle phalanges of lateral four toes
Innervation
- deep peroneal nerve (L5,S1)
Function
- extension of lateral four toes
- dorsiflexion of foot
Peroneus tertius (normally considered part of EDL) (PT)
Origin
- Third quarter of anterior surface of fibula
Insertion
- Dorsomedial surface of shaft and base of 5th metatarsal
Innervation
- Deep peroneal nerve (L5,S1)
Function
- Dorsiflexion of foot
- Eversion of foot
Arterial supply
Anterior tibial artery
- Originates from bifurcation of popliteal artery in posterior compartment of the leg under the fibrous arch of soleus at distal border of popliteus
- Passes anteriorly between the heads of tibialis posterior above the upper border of the interosseous membrane
- Passes medial to neck of fibula
- Descends through the anterior compartment on the interosseous membrane.
- Runs between TA (medially) and EDL (laterally).
- Leaves the leg passing anteriorly to the distal end of the tibia and continues onto the dorsal aspect of the foot as the dorsalis pedis artery
- Then passes between TA and EHL
- The DPN initially starts lateral to the artery higher up in the leg, but crosses anterior to it halfway down the leg and winds laterally to it under the extensor retinaculum.
- In proximal leg, has a recurrent branch with connects with anastamotic network of vessels around the knee joint.
- Distally, gives rise to anterior medial malleolar artery and anterior lateral malleolar artery
Venous supply
Venae comitantes (deep veins follow the arteries and have similar names)
- The anterior tibial vein runs in close proximity to the artery
- Anastomosing set of veins running paired with the femoral artery
Nerves
Deep peroneal nerve (L4, L5)
Origin
- Arises in lateral compartment of leg as one of two divisions of common peroneal nerve (CPN)
- Which is a branch of sciatic nerve
- Which is derived from L4, L5, S1, S2 roots
- Which is a branch of sciatic nerve
- Arises deep to peroneus longus and passes forward deep to the muscle to wind around the fibula
- Passes through the anterior intermuscular septum
- Passes deep to EDL, lying between it and TA, lying on the interosseous membrane in the upper 1/4 of the leg
- It then lies between TA and EHL in the lower 3/4 of the leg, running down with the anterior vascular structures
- It passes anterior to the ankle joint between the anterior tibial artery (medially) and EDL (laterally) and beneath the extensor retinaculum
- Innervates all muscles of anterior compartment
- Continues onto dorsal foot where it innervates extensor digitorum brevis and contributes to the innervation of the first two dorsal interossei.
- Cutaneous supply is the skin overlying the 1st dorsal webbed space
Cutaneous supply of the skin overlying the anterior compartment
Lateral sural cutaneous nerve and saphenous nerve
Clinical relevance
Foot drop
- Inability to dorsiflex foot
- Typical cause is damage to the common peroneal nerve
Common peroneal nerve injury
- Susceptible to injury as passes around the lateral aspect of the neck of the fibula:
- From direct trauma
- Secondary to knee injury
- From proximal fibular fracture
- Iatrogenic during surgery
References
Torlincasi AM, Lopez RA, Waseem M. Acute compartment syndrome, 2017
Drake, R. L., Vogl, W., Mitchell, A. W. M., Gray, H., Tibbitts, R., Richardson, P., & Horn, A. (2020). Gray’s Anatomy for Students (4th ed.). Elsevier.
Dalley, A. F., Agur, A. MR., & Moore, K. L. (2023). Clinically Oriented Anatomy (9th Edition). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins USA.
Lezak, B., & Summers, S. (2020). Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Leg Anterior Compartment. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539725/
Whitaker, R. H., Borley N. R. Instant Anatomy (2nd ed.)
Au>Author contributions
May Nichols, MD2 medical student, Western Health 2024
Matthew Sun, Orthopaedic resident, Western Health 2024
